GitLab + GitLab CI with DTM Tools¶
DevStream has two abstractions: Tools and Apps.
The previous use case uses Apps. We can also achieve the same result with Tools, and here's how:
ENV Vars¶
The following environment variables are required for this to work:
Config File¶
YAML
config:
state:
backend: local
options:
stateFile: devstream.state
vars:
gitlabUser: YOUR_GITLAB_USERNAME
dockerUser: YOUR_DOCKERHUB_USERNAME
app: testapp
tools:
- name: helm-installer
instanceID: argocd
- name: repo-scaffolding
instanceID: myapp
options:
destinationRepo:
owner: [[ gitlabUser ]]
name: [[ app ]]
branch: master
scmType: gitlab
# set env GITLAB_TOKEN
token: [[ env GITLAB_TOKEN ]]
sourceRepo:
org: devstream-io
name: dtm-repo-scaffolding-python-flask
scmType: github
- name: gitlab-ci
instanceID: flask
dependsOn: [ "repo-scaffolding.myapp" ]
options:
scm:
owner: [[ gitlabUser ]]
name: [[ app ]]
branch: master
scmType: gitlab
token: [[ env GITLAB_TOKEN ]]
pipeline:
language:
framework: flask
name: python
imageRepo:
user: [[ dockerUser ]]
# set env IMAGE_REPO_PASSWORD
password: [[ env IMAGE_REPO_PASSWORD ]]
- name: argocdapp
instanceID: default
dependsOn: [ "helm-installer.argocd", "gitlab-ci.flask" ]
options:
app:
name: [[ app ]]
namespace: argocd
destination:
server: https://kubernetes.default.svc
namespace: default
source:
valuefile: values.yaml
path: helm/[[ app ]]
repoURL: ${{repo-scaffolding.myapp.outputs.repoURL}}
token: [[ env GITLAB_TOKEN ]]
imageRepo:
user: [[ dockerUser ]]
password: [[ env IMAGE_REPO_PASSWORD ]]
Update the "YOUR_GITLAB_USERNAME" and "YOUR_DOCKERHUB_USERNAME" in the above file accordingly.
Notes:
Your GitLab must have shared runners to run gitlab-ci, If you want to create a runner automatically, you can refer to gitlab-ci plugin docs about how to generate a runner by DevStream.
Run¶
First, initialize:
Bash
# this downloads the required plugins, according to the config file, automatically.
dtm init -f config.yaml
Then we apply it by running:
Now we can see the repo has been created in GitLab and the image has been uploaded to Dockerhub.
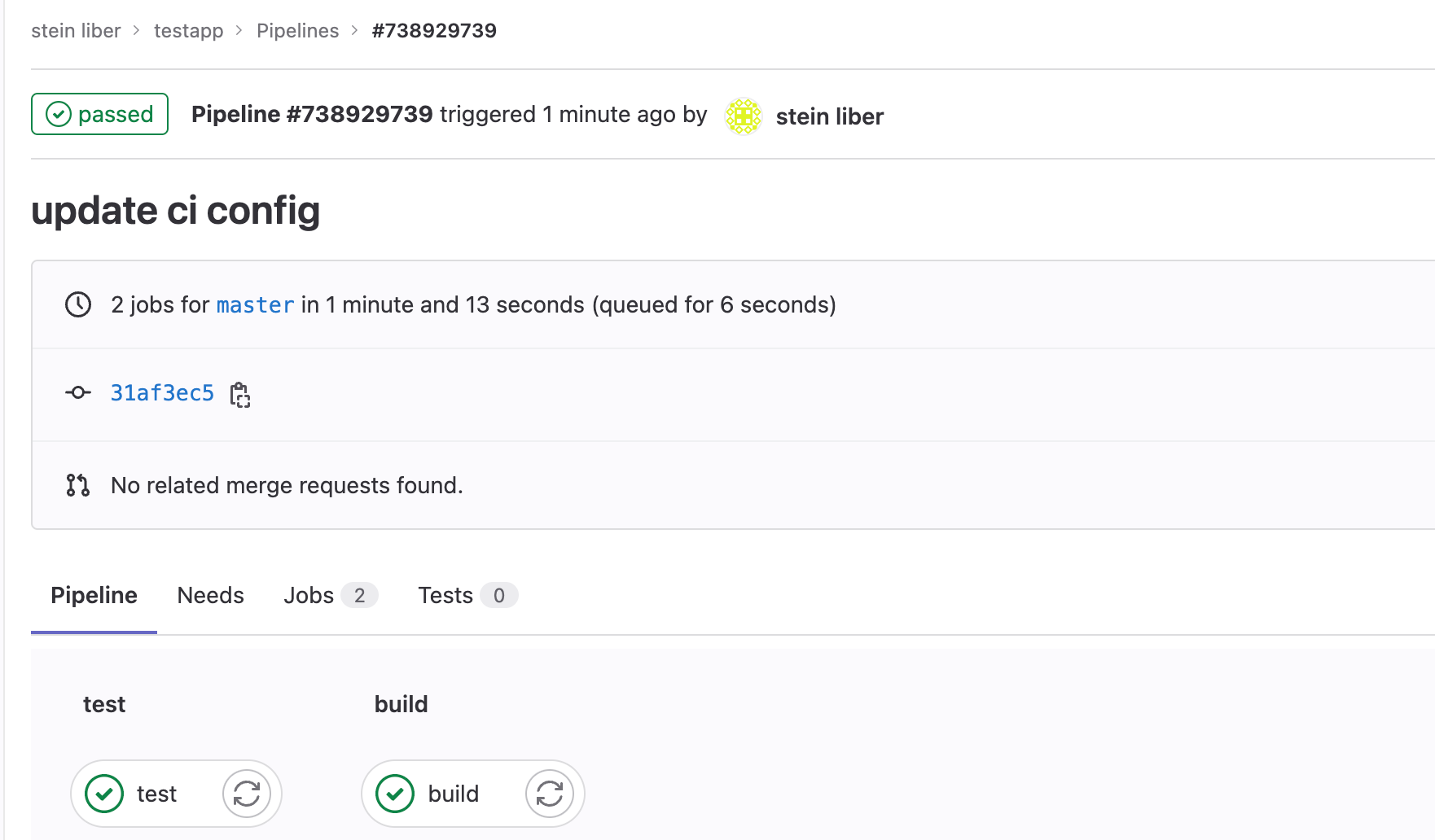
In your Kubernetes cluster, the app pod is created in the default namespace.